Overall Equipment Effectiveness
This is one of the performance measures to assess the effectiveness of your critical equipment or manufacturing line. Through this one measure, you shall holistically understand the utilization, people efficiency, and quality of product. One of the powerful operational excellence measurements
ABC Analysis
This analysis helps to put the different control mechanism of your inventory.Basically, this helps to classify your inventory into high value consumption items, low value consummation items and medium value consumption items.Based on the classification, you can implement different inventory control measures like norm settings, storage Qty, ordering frequency, reporting and reviews etc.
Root Cause Analysis
For any problem, there could be many causes contributing to the effect. This root cause analysis helps to list down all the possible causes in structured formats and then validating each cause, filtering the possible causes into probable causes and each probable cause, going in-depth to understand the root. Some of the tools and techniques are used in Root cause analysis are brainstorming, cause and effect diagram, why why analysis etc.
Total Employee Engagement
This is a concept to involve or engage all the employees towards contributing the organizational goal. Each level of employees needs different engagement, motivation and their contribution level towards an organizational goal is different, this involves designing and execution of various engagement drives, forums, initiatives, rewards and recognition etc... Some of the popular engagement initiatives are suggestion schemes, small group activities, cross-functional team participation etc.
Small Group Activities
As part of total employee engagement, in these small group activities, employees are encouraged to form a team to solve particular organizational problems, plan and execute the solutions to the problem, being recognized and dissolve the team. Primarily it is targeted at front line operators and administrators to resolve the problems relating to their work areas. areas. Most of the small group activities use simple, structured problem solving methodologies, tools and techniques under the guidance of a leader.
Key Performance Indicators (KPI)
There could be so many activities you may be performing and watching.But at the end of the day, only few activities, and its effectiveness matters to organizational profitability and growth. This Key performance indicator (KPI) as the term itself implies identifies important parameters at business level, functional level.Those parameters are specified with the right unit of measure, current level, and desired target level.
Quick Changeover Techniques
One of the wastes in any manufacturing or service system is time loss due to change over from one product type to another type. This changeover loss can happen in a machine like die setting, tool settings, comp replenishment in assembly and so on.Changeover loss is the time loss between producing last pieces of product A to the first good piece of product B. This changeover loss is significant in certain manufacturing or service system. This quick changeover technique comes with a structured way of organizing the changeover process. Some of the concepts are single minute exchange of dies (SMED), one touch exchange of dies (OTED).
Structured Problem Solving Methodologies
The tendency to solving problem is quick fix and move on, later stage again working on the same problem as fire fighting mindset. This structured problem solving methodologies comes with a systematic process of solving any problem. The typical steps include defining the problem, data collection, prioritization, analysis of causes, root cause analysis, defining action plan, implementing the action plan, check the results, and then again take the counter measures until reaching the desired solution.
There are various methodologies and approaches available to solve problems like six sigma approach, 8D, traditional problem solving using QC tools and techniques.Fundamentally, all the methodologies use the P-D-C-A approach only
Pareto Principle
This principle is also known as 80 / 20 rule for approaching any problem. It is based on the assumption that roughly 80 % of the effect come from 20 % of the causes. This principle can be applied for any problems like revenue maximization, cost reduction, quality improvement etc.
Mistake Proofing Techniques
In any human work, there is chance for making errors. This mistake proofing techniques aims to prevent the error at the source or at least detect the error after it occurred so that it would not be passed to the next stage or customer. This technique comes with different ideas to prevent or detect the error at the source. This can be applied any environment where there is scope for human error.
Visual Management
One of the powerful concepts in management is visual management. It consists of visual display, visual metrics and visual controls. Effective planning and implementation of visual management systems helps in improving communication, problem exposing and solving at the right time, improving the people engagement across the organization. It can be applied in both manufacturing and service areas as well
Principles of ergonomics
One of the micro productivity tools is an application of ergonomics. This discipline mainly concerns about the human and work relationship.Mainly its focus on optimizing the four factors like person, tool, work and environment.
Talent Mapping
One of the strategic and tactic tool for people development. This will help to map the people on potential and performance basis. This will help to diagnose the organizational person's strength as well as to plan the development plan for the individual.This mapping requires a high level of maturity and judgment.
Competency Mapping
One of the tools is to assess and map the skill, knowledge, and behavior requirement for a particular position and the incumbent existing level. This will help to develop the competency of individual through either online or offline training, coaching, mentoring etc.
Value Stream Mapping
This lean visualization technique will help to map the entire supply chain process from end to end. This will help to see the current state of the material flow, process flow and information flow across the organization. It also helps to identify the waste elimination or reduction opportunities at the big picture level. This can be used as a blueprint for future improvements of organizational supply chain activities.This is the basis before starting any lean initiatives in the organization.
Project Management
Other than operational activities, all activities can be considered as a project. This project management discipline comes with a set of techniques, methodologies to plan and execute the projects to achieve planned, on time execution, planned quality achievements, and planned. Cost targets. The knowledge, tools and techniques of project management can be applied for new product development, new plant expansion or initiating any new change management initiatives.
The Cost of Quality
This one of the holistic measures of cost associated with product and service quality in the organization. This measure helps to see the cost associated with quality in different perspectives and helps to drive the organization holistically on improvising the quality in each stage than looking at the cost of quality in isolated functions or areas.
Maintenance Management
This management is all about effective usage of assets like machinery and utilities. This covers the aspects of breakdown maintenance, preventive maintenance, planned maintenance, empowering the operation people to own the equipment, spares management, reliability maintenance etc.
Quality Assurance
This is more about ensuring quality built at each stage of product development and manufacturing process rather than controlling the quality at each stage.It is more about engineering, problem solving at source, culture building on continuous improvement, proactive management than reactive management.
Inventory Turn
One of the basic measures of inventory management. It measures the efficiency of inventory level w.r.t organizational sales level. It is measured as the ratio of sales Qty to average inventory level at a given time. This measure helps to track how efficiently management rotates the inventory stock w.r.t sales
Break Even Analysis
Break even analysis is important to plan your finance and cost management.The breakeven point is when you get neither profit nor loss, beyond break even, you generate positive cash flow or profit. This analysis is required whenever you are planning for expansion, new product introduction or even in your existing business. This will help to plan your production or sales, expenses and even your working capital.
Lost Order Analysis
Lost order Analysis is all about analyzing the past orders, which you lost to competition. This analysis on a frequent basis will help you to get new insight on competition, pricing, internal flexibility and from that learning, you can change your strategy and tactics to convert the potential customers into regular ones.
Flow Manufacturing
One of the lean manufacturing concepts, where in you are converting RM into FG with minimal or no delay in the flow. Single piece flow is one of the idealistic measures of flow manufacturing. To bring the idealistic state of single piece flow, you need to improve on imbalance factor in your production rate, rejection control, equipment utilization, and work standardization, plant layout improvement, communication improvement etc.The ultimate business measure is lead-time reduction from the day you receive order to fulfilling the order to customer.
Line Balancing
One of the flow manufacturing techniques is balancing the production line or cell w.r.t Takt Time or customer pace.
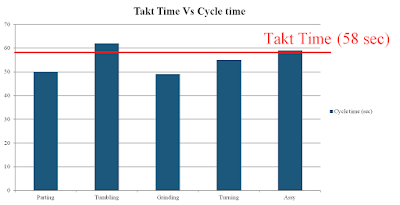
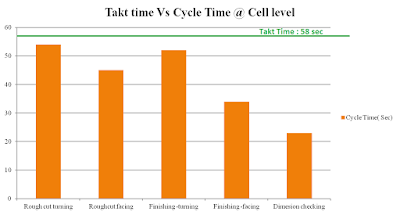
Takt Time
TAKT time is defined time at which rate customer is expecting his product to be produced. For example, if takt time is 1 min, the customer is expecting one product must be rolled out every one min.Accordingly, you need to internally balance your entire manufacturing process within or equal to 1 min.
Lead Time
Lead time is the time the system takes to deliver the product or service from the moment you receive the order to deliver to the customer. It comprises both value added and non value added activities . This lead-time reduction must be one of your key performance indicators as this reflects the system efficiency in totality.
Cycle Time
This is the time taken to produce one item. It consists of value added time. Your focus must be on reducing the process cycle time if it is constraint for delivery
Changeover Time
The time elapsed between the good products produced of comp one to the good product produced of comp 2. It includes setting of tools/ dies and adjustments of equipment or tool to achieve the quality requirement of the product.
Product Vs Process Layout
The way the plant equipments, processes organized in terms of process or product layout has major implication on your material flow, lead time and information flow.The plant layout has to be reloaded depends on the product varieties and volume.
Housekeeping Principles
The fundamental of operational excellence is keeping the house in order. The important principles of housekeeping are as follows
• Keep what you really need
• Provide a location for each part
• Provide identification for each part
• Establish process for cleaning and sustaining
Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA)
One of the quality assurance tools which can be used for existing and new design and process. It is basically looking at the risk associated with the design or process from the customer‘s perspective. The risk can be primarily related to quality and safety. This tool can be used in design, process and service area as well.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Statistical process control is a method of quality control, which uses statistical methods to monitor, and control a process.SPC can be applied in any manufacturing process where the process parameter can be measured against the target specification. This can be taught to operating people and quality can be controlled at source level.
Control Charts
Control charts are Statistical process control (SPC) tool used to determine if a manufacturing or business process is in a state of control or not. There are various types of control charts depending on the process observation type viz variables and attributes. This can be taught to operating people and quality can be controlled at source level.
Gantt chart
A simple visual tool that shows the plan vs actual status of any activity at any given time.It can be used for tracking the progress of actions in project environment as well as in an operational environment.
Why Why Analysis
One of the technique to find the root cause of the problem is why why analysis. In this method, each probable cause will be questioned to deeper level to get the root cause of the problem.
Factory Master Plan
The factory master plan is a strategic planning process in which you are planning your future business, say 3-5 yrs timeline from all perspectives. This will help to plan your resources like finance, people, capability improvement etc. This is a dynamic process and needs to be done periodically
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing system can be understood by relating to the human body. If the person appears “lean”, then the general assumption is that he/she is free from unnecessary FAT in the body, hence free from unnecessary side effects like BP, Pain in joints, laziness etc. And the person is perceived as healthy, more flexible, active etc.
The same way ,Lean manufacturing means , manufacturing system is free from unnecessary fats like high inventory, high rejection, high breakdowns or line stoppages factors etc which leads to more flexible in delivery, less lead time, first time right , low cost of manufacturing and free flow of communication etc .
Lean System Thinking
Lean System or Lean Organization means free from unnecessary waste in the entire value chain starting from extended supply chain system to the customer, even after sales service system.
Lean system Thinking is more than the application of Tools and Techniques.
It is a culture of continuous improvement or a way of working or winning mindset of everyone working for the organization.
Value Chain analysis
This is one of the management initiatives to understand the cost stack up in each product and analyzing the opportunity to take out the cost through kaizen, process improvement, waste elimination or reduction, material yield improvements, supply chain initiatives etc.
Product Pricing Analysis
A Systematic analysis of cost stack up in product cost and identifying opportunity for cost takeout without affecting the customer’s deliverables
SWOT Analysis
A systematic assessment of organizational strength, weakness, opportunity and threat from marketing, product, people, resource point of view. This is strategic, dynamic process and needs to be done periodically by the senior leadership team.
This is one of the performance measures to assess the effectiveness of your critical equipment or manufacturing line. Through this one measure, you shall holistically understand the utilization, people efficiency, and quality of product. One of the powerful operational excellence measurements
ABC Analysis
This analysis helps to put the different control mechanism of your inventory.Basically, this helps to classify your inventory into high value consumption items, low value consummation items and medium value consumption items.Based on the classification, you can implement different inventory control measures like norm settings, storage Qty, ordering frequency, reporting and reviews etc.
Root Cause Analysis
For any problem, there could be many causes contributing to the effect. This root cause analysis helps to list down all the possible causes in structured formats and then validating each cause, filtering the possible causes into probable causes and each probable cause, going in-depth to understand the root. Some of the tools and techniques are used in Root cause analysis are brainstorming, cause and effect diagram, why why analysis etc.
Total Employee Engagement
This is a concept to involve or engage all the employees towards contributing the organizational goal. Each level of employees needs different engagement, motivation and their contribution level towards an organizational goal is different, this involves designing and execution of various engagement drives, forums, initiatives, rewards and recognition etc... Some of the popular engagement initiatives are suggestion schemes, small group activities, cross-functional team participation etc.
Small Group Activities
As part of total employee engagement, in these small group activities, employees are encouraged to form a team to solve particular organizational problems, plan and execute the solutions to the problem, being recognized and dissolve the team. Primarily it is targeted at front line operators and administrators to resolve the problems relating to their work areas. areas. Most of the small group activities use simple, structured problem solving methodologies, tools and techniques under the guidance of a leader.
Key Performance Indicators (KPI)
There could be so many activities you may be performing and watching.But at the end of the day, only few activities, and its effectiveness matters to organizational profitability and growth. This Key performance indicator (KPI) as the term itself implies identifies important parameters at business level, functional level.Those parameters are specified with the right unit of measure, current level, and desired target level.
Quick Changeover Techniques
One of the wastes in any manufacturing or service system is time loss due to change over from one product type to another type. This changeover loss can happen in a machine like die setting, tool settings, comp replenishment in assembly and so on.Changeover loss is the time loss between producing last pieces of product A to the first good piece of product B. This changeover loss is significant in certain manufacturing or service system. This quick changeover technique comes with a structured way of organizing the changeover process. Some of the concepts are single minute exchange of dies (SMED), one touch exchange of dies (OTED).
Structured Problem Solving Methodologies
The tendency to solving problem is quick fix and move on, later stage again working on the same problem as fire fighting mindset. This structured problem solving methodologies comes with a systematic process of solving any problem. The typical steps include defining the problem, data collection, prioritization, analysis of causes, root cause analysis, defining action plan, implementing the action plan, check the results, and then again take the counter measures until reaching the desired solution.
There are various methodologies and approaches available to solve problems like six sigma approach, 8D, traditional problem solving using QC tools and techniques.Fundamentally, all the methodologies use the P-D-C-A approach only
Pareto Principle
This principle is also known as 80 / 20 rule for approaching any problem. It is based on the assumption that roughly 80 % of the effect come from 20 % of the causes. This principle can be applied for any problems like revenue maximization, cost reduction, quality improvement etc.
Mistake Proofing Techniques
In any human work, there is chance for making errors. This mistake proofing techniques aims to prevent the error at the source or at least detect the error after it occurred so that it would not be passed to the next stage or customer. This technique comes with different ideas to prevent or detect the error at the source. This can be applied any environment where there is scope for human error.
Visual Management
One of the powerful concepts in management is visual management. It consists of visual display, visual metrics and visual controls. Effective planning and implementation of visual management systems helps in improving communication, problem exposing and solving at the right time, improving the people engagement across the organization. It can be applied in both manufacturing and service areas as well
Principles of ergonomics
One of the micro productivity tools is an application of ergonomics. This discipline mainly concerns about the human and work relationship.Mainly its focus on optimizing the four factors like person, tool, work and environment.
Talent Mapping
One of the strategic and tactic tool for people development. This will help to map the people on potential and performance basis. This will help to diagnose the organizational person's strength as well as to plan the development plan for the individual.This mapping requires a high level of maturity and judgment.
Competency Mapping
One of the tools is to assess and map the skill, knowledge, and behavior requirement for a particular position and the incumbent existing level. This will help to develop the competency of individual through either online or offline training, coaching, mentoring etc.
Value Stream Mapping
This lean visualization technique will help to map the entire supply chain process from end to end. This will help to see the current state of the material flow, process flow and information flow across the organization. It also helps to identify the waste elimination or reduction opportunities at the big picture level. This can be used as a blueprint for future improvements of organizational supply chain activities.This is the basis before starting any lean initiatives in the organization.
Project Management
Other than operational activities, all activities can be considered as a project. This project management discipline comes with a set of techniques, methodologies to plan and execute the projects to achieve planned, on time execution, planned quality achievements, and planned. Cost targets. The knowledge, tools and techniques of project management can be applied for new product development, new plant expansion or initiating any new change management initiatives.
The Cost of Quality
This one of the holistic measures of cost associated with product and service quality in the organization. This measure helps to see the cost associated with quality in different perspectives and helps to drive the organization holistically on improvising the quality in each stage than looking at the cost of quality in isolated functions or areas.
Maintenance Management
This management is all about effective usage of assets like machinery and utilities. This covers the aspects of breakdown maintenance, preventive maintenance, planned maintenance, empowering the operation people to own the equipment, spares management, reliability maintenance etc.
Quality Assurance
This is more about ensuring quality built at each stage of product development and manufacturing process rather than controlling the quality at each stage.It is more about engineering, problem solving at source, culture building on continuous improvement, proactive management than reactive management.
Inventory Turn
One of the basic measures of inventory management. It measures the efficiency of inventory level w.r.t organizational sales level. It is measured as the ratio of sales Qty to average inventory level at a given time. This measure helps to track how efficiently management rotates the inventory stock w.r.t sales
Break Even Analysis
Break even analysis is important to plan your finance and cost management.The breakeven point is when you get neither profit nor loss, beyond break even, you generate positive cash flow or profit. This analysis is required whenever you are planning for expansion, new product introduction or even in your existing business. This will help to plan your production or sales, expenses and even your working capital.
Lost Order Analysis
Lost order Analysis is all about analyzing the past orders, which you lost to competition. This analysis on a frequent basis will help you to get new insight on competition, pricing, internal flexibility and from that learning, you can change your strategy and tactics to convert the potential customers into regular ones.
Flow Manufacturing
One of the lean manufacturing concepts, where in you are converting RM into FG with minimal or no delay in the flow. Single piece flow is one of the idealistic measures of flow manufacturing. To bring the idealistic state of single piece flow, you need to improve on imbalance factor in your production rate, rejection control, equipment utilization, and work standardization, plant layout improvement, communication improvement etc.The ultimate business measure is lead-time reduction from the day you receive order to fulfilling the order to customer.
Line Balancing
One of the flow manufacturing techniques is balancing the production line or cell w.r.t Takt Time or customer pace.
Takt Time
TAKT time is defined time at which rate customer is expecting his product to be produced. For example, if takt time is 1 min, the customer is expecting one product must be rolled out every one min.Accordingly, you need to internally balance your entire manufacturing process within or equal to 1 min.
Lead Time
Lead time is the time the system takes to deliver the product or service from the moment you receive the order to deliver to the customer. It comprises both value added and non value added activities . This lead-time reduction must be one of your key performance indicators as this reflects the system efficiency in totality.
Cycle Time
This is the time taken to produce one item. It consists of value added time. Your focus must be on reducing the process cycle time if it is constraint for delivery
Changeover Time
The time elapsed between the good products produced of comp one to the good product produced of comp 2. It includes setting of tools/ dies and adjustments of equipment or tool to achieve the quality requirement of the product.
Product Vs Process Layout
The way the plant equipments, processes organized in terms of process or product layout has major implication on your material flow, lead time and information flow.The plant layout has to be reloaded depends on the product varieties and volume.
Housekeeping Principles
The fundamental of operational excellence is keeping the house in order. The important principles of housekeeping are as follows
• Keep what you really need
• Provide a location for each part
• Provide identification for each part
• Establish process for cleaning and sustaining
Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA)
One of the quality assurance tools which can be used for existing and new design and process. It is basically looking at the risk associated with the design or process from the customer‘s perspective. The risk can be primarily related to quality and safety. This tool can be used in design, process and service area as well.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Statistical process control is a method of quality control, which uses statistical methods to monitor, and control a process.SPC can be applied in any manufacturing process where the process parameter can be measured against the target specification. This can be taught to operating people and quality can be controlled at source level.
Control Charts
Control charts are Statistical process control (SPC) tool used to determine if a manufacturing or business process is in a state of control or not. There are various types of control charts depending on the process observation type viz variables and attributes. This can be taught to operating people and quality can be controlled at source level.
Gantt chart
A simple visual tool that shows the plan vs actual status of any activity at any given time.It can be used for tracking the progress of actions in project environment as well as in an operational environment.
Why Why Analysis
One of the technique to find the root cause of the problem is why why analysis. In this method, each probable cause will be questioned to deeper level to get the root cause of the problem.
Factory Master Plan
The factory master plan is a strategic planning process in which you are planning your future business, say 3-5 yrs timeline from all perspectives. This will help to plan your resources like finance, people, capability improvement etc. This is a dynamic process and needs to be done periodically
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing system can be understood by relating to the human body. If the person appears “lean”, then the general assumption is that he/she is free from unnecessary FAT in the body, hence free from unnecessary side effects like BP, Pain in joints, laziness etc. And the person is perceived as healthy, more flexible, active etc.
The same way ,Lean manufacturing means , manufacturing system is free from unnecessary fats like high inventory, high rejection, high breakdowns or line stoppages factors etc which leads to more flexible in delivery, less lead time, first time right , low cost of manufacturing and free flow of communication etc .
Lean System Thinking
Lean System or Lean Organization means free from unnecessary waste in the entire value chain starting from extended supply chain system to the customer, even after sales service system.
Lean system Thinking is more than the application of Tools and Techniques.
It is a culture of continuous improvement or a way of working or winning mindset of everyone working for the organization.
Value Chain analysis
This is one of the management initiatives to understand the cost stack up in each product and analyzing the opportunity to take out the cost through kaizen, process improvement, waste elimination or reduction, material yield improvements, supply chain initiatives etc.
Product Pricing Analysis
A Systematic analysis of cost stack up in product cost and identifying opportunity for cost takeout without affecting the customer’s deliverables
SWOT Analysis
A systematic assessment of organizational strength, weakness, opportunity and threat from marketing, product, people, resource point of view. This is strategic, dynamic process and needs to be done periodically by the senior leadership team.