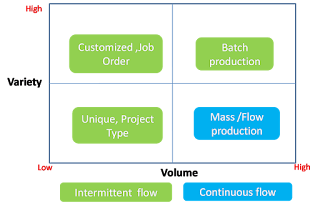
Any manufacturing organization can be classified based on the production system. The production system is primarily based on TWO factors
1. Volume
2. Variety.
As shown in Pic, any organizations production system falls under any of the categories
1.Unique / Project Type production
2.Customized, Job Order production
3.Standardised, Batch Type production
4.Mass / Flow Production
You can fit your organization production system in any one of the above production systems.
However, irrespective of your production system, what matters for business profitability is SEAMLESS FLOW.
The ultimate objective of any organization is to striving towards continuous flow from the upstream process( RM Procurement from suppliers) to downstream process ( FG dispatch to customers).
How is the flow measured in manufacturing?
Flow is measured as Lead time. (Definition of lead time)
why flow is affected in any production system?
Impact of poor flow on the business :
Continuous improvement efforts to integrate all elements of the production system.
The goal is a best possible balanced production line with little waste, the lowest possible cost, on-time and defect-free production.
Benefits of Continous flow improvement approach is as follows
To sum up, irrespective of your production system, you need to continuously improve the flow for sustainable business profitability !
1. Volume
2. Variety.
As shown in Pic, any organizations production system falls under any of the categories
1.Unique / Project Type production
2.Customized, Job Order production
3.Standardised, Batch Type production
4.Mass / Flow Production
You can fit your organization production system in any one of the above production systems.
However, irrespective of your production system, what matters for business profitability is SEAMLESS FLOW.
The ultimate objective of any organization is to striving towards continuous flow from the upstream process( RM Procurement from suppliers) to downstream process ( FG dispatch to customers).
How is the flow measured in manufacturing?
Flow is measured as Lead time. (Definition of lead time)
why flow is affected in any production system?
- Cycle time imbalance between work center
- Rejections / rework at each stage
- Machine Breakdowns
- Changeovers or setting time
- Lack of resources (material/man)
- waiting for decisions
Impact of poor flow on the business :
- WIP between work centers
- Long lead time
- More Space
- More Movements and Handling efforts
- Rejections / Rework
- Communication issues
- Low productivity
- Low flexibility to the customer
Solutions approach to improving flow in ANY production system:
Continuous-flow manufacturing (CFM) is an approach
The goal is a best possible balanced production line with little waste, the lowest possible cost, on-time and defect-free production.
- WIP inventory reduction
- Space utilization
- Set up time reduction
- Lead time reduction
- Reduce material handling distance
- Productivity improvement
- Quality improvement
- Better teamwork and communication
- High Flexibility
- Better Visibility
To sum up, irrespective of your production system, you need to continuously improve the flow for sustainable business profitability !